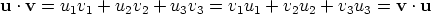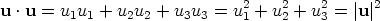|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
9. The scalar product
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Suppose u, v and w are vectors (in the plane or in space) with magnitudes |u|, |v| and |w|. Then 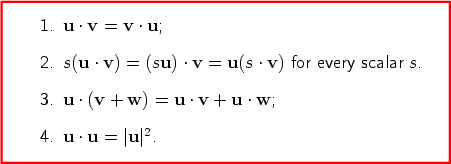
The rules are obtained by using the Cartesian representation of the scalar product. We let u = u1i + u2j + u3k, v = v1i + v2j + v3k and w = w1i + w2j + w3k. Then
Alternatively one could prove the algebraic rules using the Cartesian representation of the scalar product.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Feedback |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
© 2002-09 The University of Sydney. Last updated: 09 November 2009
ABN: 15 211 513 464. CRICOS number: 00026A. Phone: +61 2 9351 2222.
Authorised by: Head, School of Mathematics and Statistics.
Contact the University | Disclaimer | Privacy | Accessibility