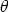|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
9. The scalar product
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
By definition of the scalar product, u·v = |u||v| cos 
If u = u1i + u2j + u3k and v = v1i + v2j + v3k are given in Cartesian form then the above reads 
For vectors in the plane drop the third terms.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Feedback |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
© 2002-09 The University of Sydney. Last updated: 09 November 2009
ABN: 15 211 513 464. CRICOS number: 00026A. Phone: +61 2 9351 2222.
Authorised by: Head, School of Mathematics and Statistics.
Contact the University | Disclaimer | Privacy | Accessibility